May 9, 2025
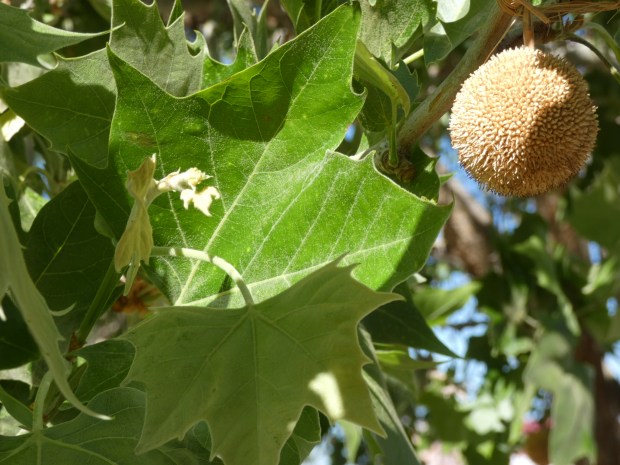

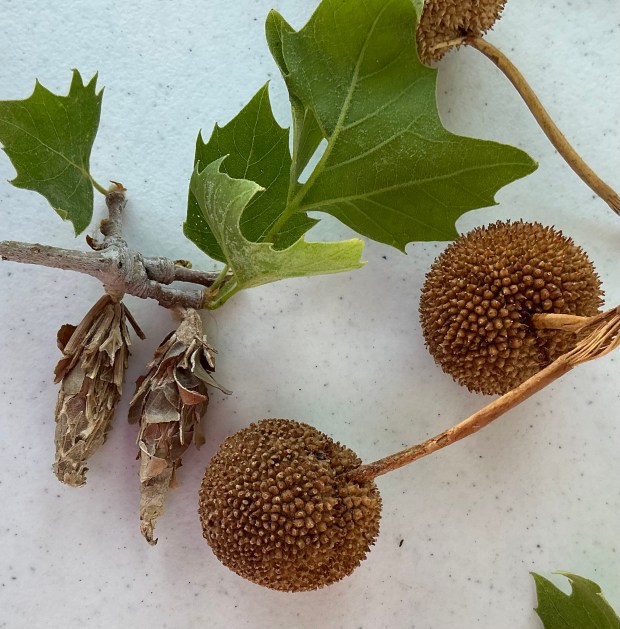
On a warm Spring morning, wandering around a grove of American Sycamore, I became curious about these magnificent trees: where in the US are they native; why are some leaves larger than the palm of my hand and some half the size; what about those odd pingpong sized seedballs lying on the ground everywhere you look ….. why don’t they roll away in search of an ideal spot to pop open so the seeds can germinate …… when the seedballs are kicked, stepped on or crushed beneath a car tire, do the 1,000’s of seeds inside blow away to sprout ….. are the seeds (all or some of them) even viable ….. do the seedballs make a good ink or dye or maybe they’re edible or even medicinal……. what, if any wildlife species eat the seedballs or seeds; and ooooohhhhhhh, sycamore bark! Why does this tree’s bark flaunt a pastel palette of greens, yellows and pinks. These and many more questions came to mind that it seemed about time the American Sycamore became a subject for my nature journal, until ……………..

There! In the tree above my head, I spotted a most curious thing. Parting a few of that sycamore’s beautiful Spring green palmate-shaped leaves was a bundle of dead brown and beige leafy bits and sticks all haphazardly glued together. Wishing to get a closer look at that elongated ornament shaped “thing,” I found it was securely suspended from a branch. Trying to puzzle out this fascinating mystery while searching for my pen knife, a stiff breeze blew through the tree. It was then a I noticed hundreds of those 2-3” long bundles all over the tree; from the base to its crown!
Curiosity is the Essence of Nature Journaling
What continues to draw me to nature and nature journaling after so many years are the surprises in the familiar and in the unknown. I know well enough that new encounters in nature are infinite; you just have to open your eyes and look. Having learned by carefully observing what appears to be familiar, often leads to new discoveries. That’s when my curiosity kicks into high gear ….. when it’s time to engage in some serious poking around to figure something out; to learn what the “thing” is.
Curiosity, for me, is the very heart and soul of nature journaling. The ‘art’ of curiosity even precedes skill in observation. It’s what drives me out the door in the morning and fuels my exploration. Curiosity fills the mind with countless questions if for no other reason but to develop a deeper understanding of the natural world.
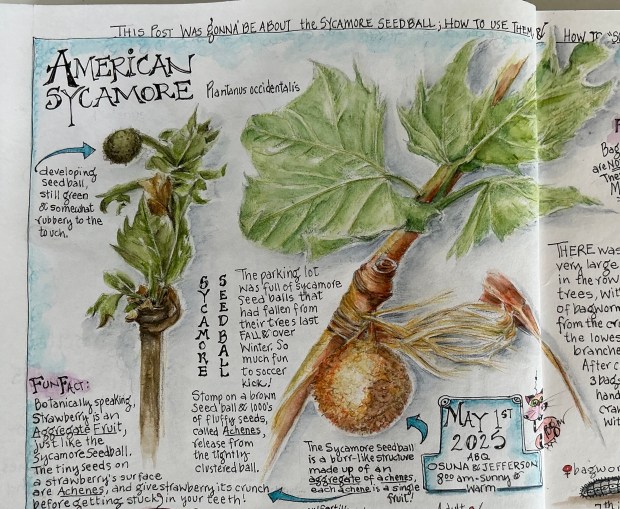
But I “wax philosophical.” Needless to say, my curious discovery on that warm and breezy Spring morning prompted an abrupt change of mind for my next blog post (this post). Anxious to learn about the “thing” suspended from a tree branch, probably minding its own business, I proceeded to cut it down (along with two more) and popped them in a bag along with a few sycamore leaves and seedballs.
Later that same day …….
Upon completing my journal sketches of sycamore leaves and seedballs, and posting a few photos to iNaturalist for an initial ID, it was time to take a closer look at my discovery. Reaching into the bag for one of the “things” (wiping my hand free of spider webbing?), I placed it on my examination table surrounded by several hand lenses, a larger magnifying glass, a penknife, and 2 pairs of tweezers. Before beginning the dissection, I noticed about a dozen black pepper-sized bits moving about the “thing.” Thinking tiny spiders had come from the bag, I didn’t give them a second thought (should’ve been curious!).
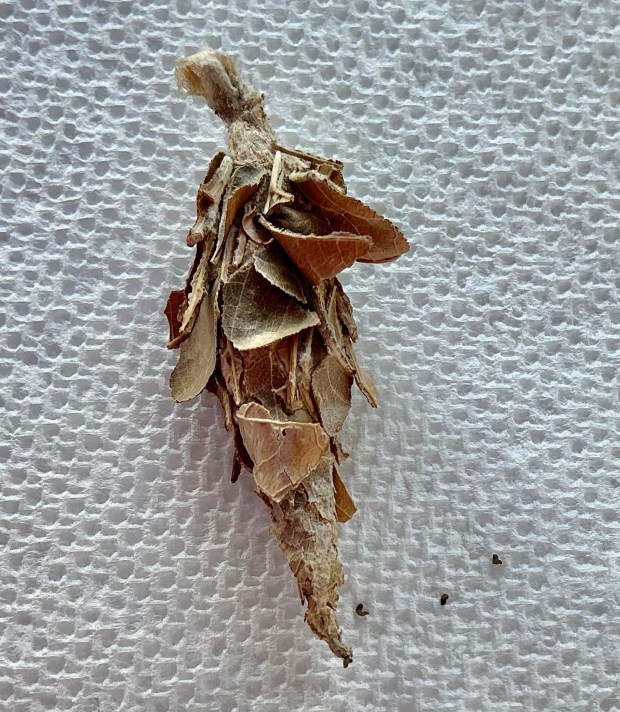

iNaturalist ID Pick :::::::::::::: BAGWORM MOTH ::::::::::::::: iNaturalist ID Pick
(awaiting genus/species ID)
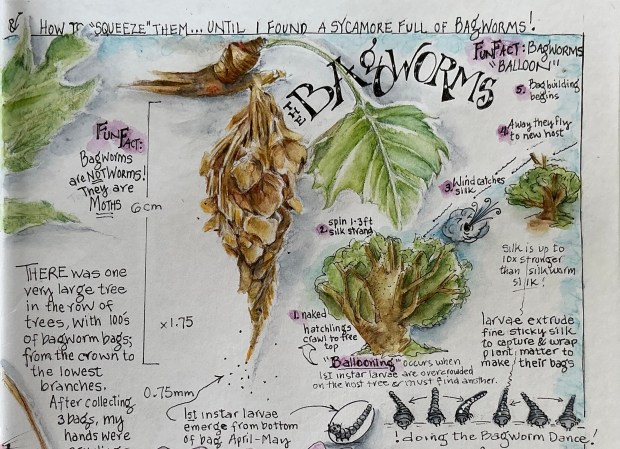
A Bagworm Moth!
How cool is that!?!
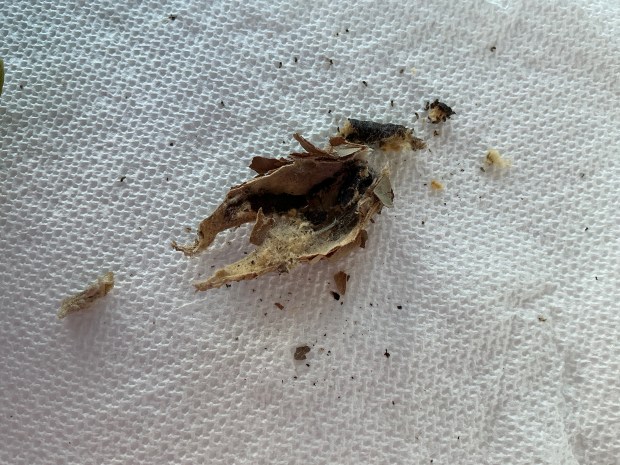

Dissection resumes ……
After finding out the “thing” I’ve been pondering over is the Bag of a bagworm moth, I learned the Bag was built during last Spring, Summer and Fall by either a male or female bagworm moth. If a male, the Bag would be empty; if a female, the Bag would contain her remains …. she would’ve died last fall after a male fertilized 500-1,000+ eggs she overwintered inside her body until Spring when newly-hatched larvae would emerge from the bottom of the Bag and begin the species’ life cycle all over again.
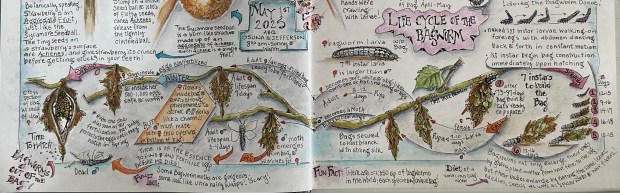


The Bag, that took about 10 minutes and all my dissection tools to open, contained the black and mushy remains of a female and 100’s of wiggling/dancing larvae! They were on the move; escaping from the now wide open Bag, and quickly covering my examination table like a pepper grinder out of control.
And my effort to open the Bag? This made sense after reading about the high tensile strength of the silk they produce. These thin strands of silk, 10x stronger than that produced by silkworms, is used in abundance to construct their Bags.

After disposing of all the naked 1st instar larvae waggling and dancing across my examination table, I placed the dissected Bag, the two whole Bags, and collected leaf material into a clear plastic ziplock to observe what would happen. Over 10 days, the number of larvae multiplied and the naked 1st instar caterpillars grew in size (at least to 2nd instar) while building their individual Bags from tiny bits of leaf litter! Their wiggling dance seemed to be the way their silk strands wrapped and secured leafy bits around their bodies. It’s been fun to watch all the activity.

Have you ever encountered one or more of the 1,350+ species of bagworm moths? What materials were their Bags made from? Please share your experience with these fascinating members of the butterfly/moth family of insects.
As always, thanks for stopping by!