August 2, 2025

Sunflowers!🌻 Absolutely the happiest flower on Earth. Wouldn’t you agree?
Sunflowers, a symbol of adoration, loyalty, and longevity, represent happiness, friendship, and intelligence. Much like the sun, sunflowers reflect vibrancy and an energy of life. While National Sunflower Day is the official day to celebrate these beautiful flowers, why not declare the entire growing season reason a-plenty to radiate your inner sunshine and mirror the smiling faces of every sunflower encountered!
Then and Now
Did you know sunflowers have been around since about 1000 BCE? In the U.S. indigenous peoples used sunflowers as a valuable food source, for oil, paint, and textiles, and during ceremonies. Some archaeologists even believe sunflowers may have been cultivated before corn. Today, sunflowers are still used for food (seeds, salad mixes) and beverages (tea), cooking oil, in beauty and skin care treatments, for medicinal purposes, and for hobbies and crafts.
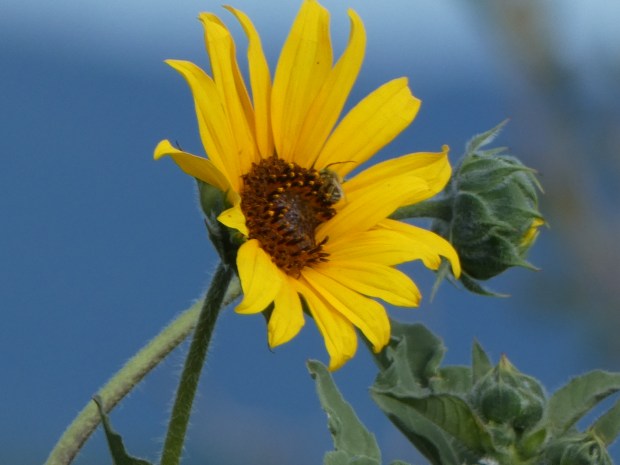

The sunflower crop
The U.S. is a mass producer of sunflowers, particularly in the plains states, and is a major crop in both North Dakota and South Dakota. The average cultivated sunflower plant is five to six feet tall, and the central face of disc flowers can grow bigger than a human head. As the weight of the sunflower head becomes heavy, it begins to fall forward causing the petals to fall off. Shortly after the harvest begins. On average, one sunflower can produce up to 2,000 seeds per head. In 2022, North Dakota produced 762 billion pounds of sunflower seeds!
The Happiest and the most Intelligent flower
Have you ever noticed sunflowers track the sun, from sunrise to sunset? It’s true! Sunflowers follow the sun’s movements throughout the day. You may notice that before sunrise, a sunflower is in sort of a sleeping position with its head slightly down. As the sun comes over the horizon, the flower awakens and slowly lifts its face to ‘look’ directly at the rising sun. As the day progresses and we observe the sun moving from east to west, so too does the sunflower by turning its face in sync with the sun’s apparent movements until sunset.1 When the sun sets in the evening, sunflowers nod off to sleep, but not before untwisting themselves and slowly return to face the east. Ingenious!
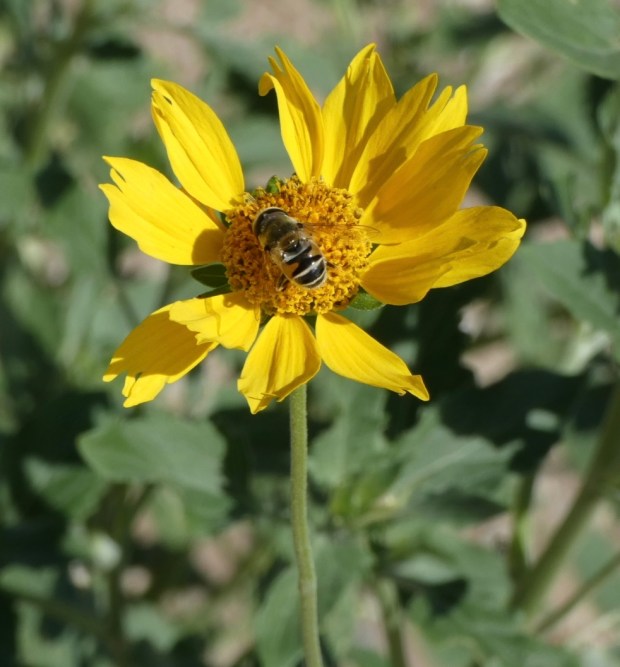

1 However, on very hot days, sunflowers tend to avoid looking directly at the sun to keep from overheating. And I’ve noticed on cloudy days, sunflowers may appear confused about the sun’s location, seeming to make their best guess on which way to face.
A season of yellows and oranges
Although you can find flowers in the Aster (sunflower) family in the Spring, August is the peak growing and blooming season for these cheerful plants. Brilliant displays of yellow flowers welcoming the morning sun can be found wherever sunflowers grow. Witnessing fields of sunflowers is guaranteed to lift your spirits as you oooooh and aaaaaaaah at their breathtaking beauty.

Ideas to celebrate a day, week, month or year of sunflowers
- Spend a day with a wild sunflower and watch its face track the sun.
- Take a drive to view fields of sunflowers to see their true beauty in mass.
- Give a bouquet of sunflowers to a friend to brighten their day.
- Add sunflower petals and seeds to your salad.
- Create a painting of your favorite sunflower and frame it to enjoy year-round.
- Try your hand at a Zentangled sunflower bouquet ….. there are as many pattern possibilities as there are blooming sunflowers!
- Plan a road trip to North Dakota in August and coordinate places to stop to visit sunflower fields and get updates from local farmers who cultivate sunflowers.
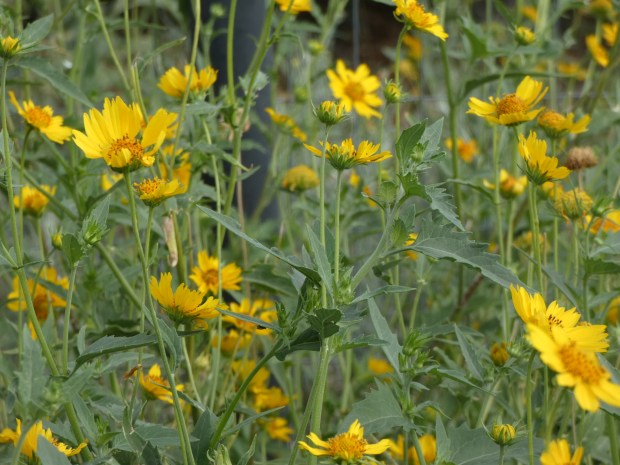

If you missed celebrating this year’s National Sunflower Day, no worries! Every time you come across any sunflower, of any size, anywhere, pause and hold a personal celebration in honor of its splendiferous magnificence!
As always, thanks for stopping by!
Sunflower photos were taken in our backyard ….. all volunteers too!