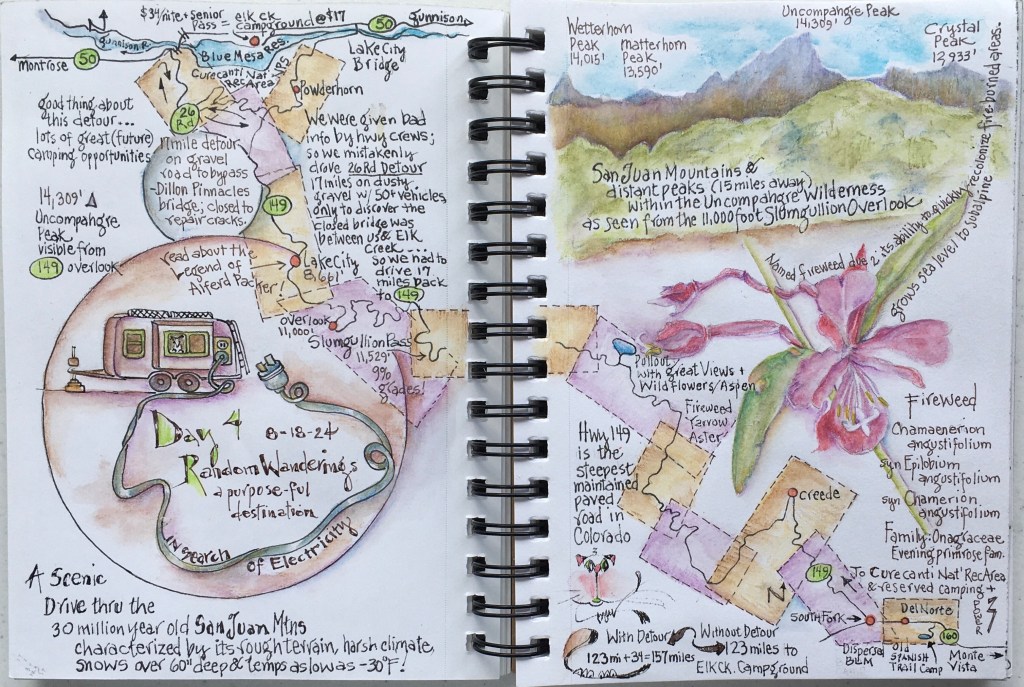
February 1, 2025
Wandering about the neighborhood one warm summer morning in 2018, I noticed a dense stand of plants lining a 20 foot section of road. What caught my eye were the umbrella-like clusters of pearly white flowers topping each slender stem. From a distance these plants resembled our native white-flowering yarrow. But I soon realized the narrow dark green leaves were not fuzzy; the tiny exotic-looking flowers were not daisy shaped. Unmistakably, this plant was a species of milkweed! And the flowers of more than 50 individual plants in this population were a-flutter and a-buzz and a-crawling with hungry insects!
What was this milkweed species?

It didn’t take long to confirm this plant as Horsetail Milkweed (Asclepias subverticillata), a species commonly found along roadsides in pinyon-juniper woodlands. Knowing what to look for on future walks, over the next several years I was excited to find 30+ more populations of various sizes along neighborhood roadways! From 2018 until early summer 2024, I continued to monitor these seemingly abundant populations. The small numbers of seeds I collected in the Fall were planted in our yard, and every year I checked for the presence, variety and numbers of insects busy feeding on nectar as they pollinated the flowers.
During June 2024, when we moved only a few miles to the northeast, I was happy to see Horsetail Milkweed grew abundantly in our new subdivision. This prompted me to dig deeper into researching this species. Its been exciting to discover how important this milkweed is to native insects, including monarch and queen butterflies.
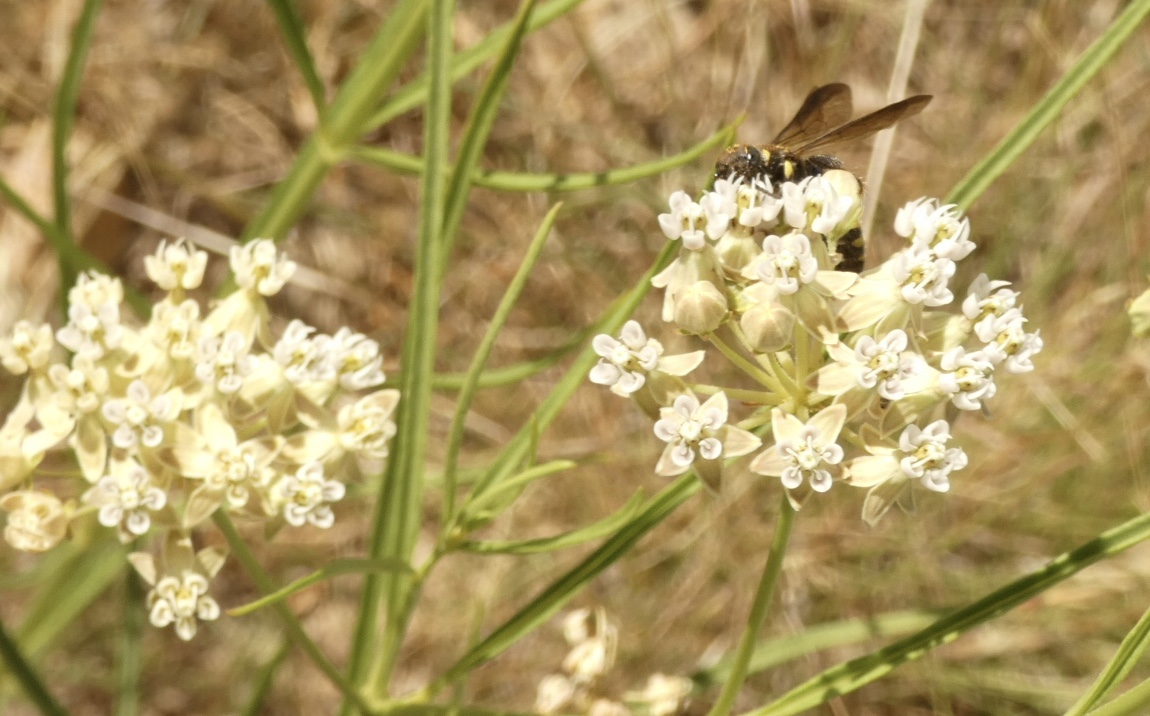

According to pollination ecologists, Horsetail Milkweed is especially valuable to large numbers of native bees. This plant species also supports conservation biological control by attracting predatory or parasitoid insects that prey upon pest insects.
And Horsetail Milkweed is one of the favorite host plants for monarch and queen butterflies, all because it’s toxic! Producing an especially nasty tasting and potent neurotoxin strong enough to kill livestock, the caterpillars of these two butterflies have evolved to benefit from such a poisonous substance. Voraciously ingesting a diet of only milkweed leaves, obviously tasty to the larvae, makes them unpalatable to would-be predators, such as birds. The toxin from milkweed leaves has become their primary means of defense; definitely a benefit for such chubby, slow little caterpillars.

Although central New Mexico isn’t in any of the major migratory routes of these butterflies, I have observed both species in our previous neighborhood. Since learning more about Horsetail Milkweed and it’s favored roadside habitat close to home, my hope is to provide actively growing plants throughout the summer (a safe distance away from roadside easements) for both the monarch and queen adult butterflies and their caterpillars ……. especially important when governing covenants of our previous and new subdivisions require the roadways be groomed (mowed down like a butch haircut!) on a monthly basis by subdivision landscape crews.
Because milkweeds are among my favorite of all plant species, mainly due to their complex flowers and the clever trickery they’ve developed to ensure pollination, I wrote about and illustrated two in-depth blog posts on this subject. Believe me when I say, “It’s overboard fascinating!”
Check out the following posts …..
Surprise! A vine-y, twine-y desert milkweed discovery from July 2024, where I revisit milkweed flower structure and pollination and learn about a new-to-me genus, Funastrum.
Summer Botany: Meet the Milkweeds from July 2022. This is my first comprehensive look at milkweed flower structure, how pollination takes place, and the genus Asclepias.
Read on to learn more botanical information about Horsetail Milkweed AND how to find out if you live in Spring and/or the Fall Migration routes of the monarch butterfly AND where queen butterflies migrate to and from.
Characteristics and habitat requirements of Horsetail Milkweed
Horsetail Milkweed is a perennial species with a stout, woody rootstock. Plants readily spread by rhizomes (underground stems) producing dense communities. Cold-hardy to at least 0℉, this milkweed bounces right back in the Spring. Plants are also drought-tolerant once established, thriving in well-drained, sandy soil under full to partial sun.
Able to thrive in a variety of habitats and plant communities from 2500 – 8000 feet in elevation, Horsetail Milkweed grows among grasses, on sandy or rocky flats, on slopes, roadsides, and along trails in Chaparral, Semidesert Grasslands, Pinyon-Juniper Woodlands, Montane Conifer Forests, and in disturbed areas.
All of these characteristics and its adaptability to a wide range of habitats make Horsetail Milkweed one of the easiest milkweed species to grow.

Monarch Butterfly
To learn if you live within the path of or close to spring and/or fall monarch butterfly migration routes, you can view a map or these route here:

Queen Butterfly
The queen is chiefly a tropical species. In the US, it is usually confined to the southern portion of the country. It can be found regularly in peninsular Florida and southern Georgia, as well as in the southern portions of Texas, New Mexico, Arizona, and California. Occasionally, the subspecies of the queen can be found somewhat north, in Kansas, Colorado and Utah.
Queen butterflies do not migrate as dramatically as monarch butterflies, but they do move short distances in tropical regions with dry seasons to higher elevations.

As always, thanks for stopping by!